12 Free GMAT Sample Questions With Explanations (for 2025)
All products and services featured are independently selected by WikiJob. When you register or purchase through links on this page, we may earn a commission.
- How to Prepare for the GMAT in 2025
- GMAT Practice Questions
empty
empty
empty
empty
- Final Thoughts
The Graduate Management Admissions Test (GMAT) is used by business schools as part of the assessment and admissions process. As a standardized exam, the GMAT allows assessors to test the applicant’s ability to work at the required level for successful study in a Masters of Business Administration (MBA) program.
The GMAT is written and delivered by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC), an international organization that represents leading business schools from around the world. More than 200,000 graduates take the GMAT every year.
The test is made up of various multiple-choice questions designed to test writing, reasoning, verbal, non-verbal and analytical skills. The answers require a knowledge of specific types of grammar, arithmetic, algebra and geometry.
The GMAT has four sections. These are:
- Integrated Reasoning (30 minutes)
- Analytical Writing Assessment (30 minutes)
- Verbal Reasoning (65 minutes)
- Quantitative Reasoning (62 minutes)
All sections draw upon analysis and critical thinking.
At the start of the test, the candidate can decide in which order to answer the questions. The orders offered are:
- Quantitative, Verbal, Integrated Reasoning, Analytical Writing Assessment
- Analytical Writing Assessment, Integrated Reasoning, Quantitative, Verbal
- Verbal, Quantitative, Integrated Reasoning, Analytical Writing Assessment
Planning the order in which to approach the sections may help candidates feel prepared and allow time to focus on areas that need more attention.
In this article, we'll look at 12 sample GMAT questions and how to arrive at the best answer for each.

How to Prepare for the GMAT in 2025
Adequate preparation is the key to completing the GMAT successfully. It is generally accepted that a candidate should start preparing eight to twelve weeks before the test is scheduled, though many candidates spend much longer than this.
Becoming familiar with the format and concept of the GMAT is the first step. It is advisable to study for one section of the test at a time, revising the key principles before going on to practice the associated questions and then moving on to the next section.
Pacing is crucial, as each portion of the test is timed. Practice tests can help candidates determine which areas they need to focus on to complete questions within the allotted time.
Practicing GMAT sample questions such as the ones demonstrated here is one of the most effective preparation techniques and would prove beneficial when integrated into a GMAT study plan.
GMAT Practice Questions
Now let’s take a look at some free GMAT sample questions for each of the four sections of the test.
1. Integrated Reasoning
The Integrated Reasoning section has a time allowance of 30 minutes and presents 12 questions covering four different areas:
- Two-Part Analysis
- Multi-Source Reasoning
- Table Analysis
- Graphics Interpretation
Question 1 – Two-Part Analysis
Two-part analysis questions require candidates to work out two components of a question, then answer from a series of possible answers laid out in a table.
| Supplier A | Supplier B | Number of Bandages |
|---|---|---|
| 500 | ||
| 1,000 | ||
| 1,500 | ||
| 2,000 | ||
| 2,500 |
A hospital wants to find a new supplier for its bandages. Supplier A makes bandages from one style of fabric, priced at $2.50 per bandage. Supplier B makes its bandages from another style of fabric, priced at $3.00 per bandage. The hospital decides to trial both types of bandage before deciding on which to use going forward. The overall budget for the trial is $10,000.
Using the table, identify exactly how many bandages the hospital needs to buy from Supplier A and Supplier B to spend the exact budget of $10,000. Place one mark in the Supplier A column and one mark in the Supplier B column.
Question 2 – Multi-Source Reasoning
Multi-source reasoning questions use several sources, usually displayed under tabs at the top or side of the page, which contain the information you will need to decide on your answers.
These questions are assessing your ability to extract information and make inferences from the text.
Mr and Mrs Smith are looking for a nursery for their son. Here are a series of emails sent between them:
Email 1:
From: Mrs Smith To: Happy Days Nursery
Hi there,
My husband and I are looking for flexible and reliable childcare for our son. We both work in high-pressure jobs which can involve unsociable hours so reliability is important to us.
Could you please let us know your availability and opening hours?
Email 2:
From: Happy Days Nursery To: Mrs Smith
Hello Mrs Smith,
Here at Happy Days, we pride ourselves on creating a warm and safe environment for our charges. Our fees are very competitive and I’m pleased to say that we do have several spaces available so your son could join us immediately. We offer a 10% discount if you sign up within 24 hours of receiving this email.
Email 3:
From: Mrs Smith To: Happy Days Nursery
We are glad to hear that our son would be in a comfortable environment and I’m sure that you do prioritize safety. The discount is good, it brings the cost down into our budget of $36 a day.
Our main concern, however, is accommodating our long and sometimes unsociable working hours, would this be possible at Happy Days Nursery?
Does the content of the emails support the inferences as stated? Answer 'yes' or 'no' for each.
- Mr & Mrs Smith are willing to pay more than they’d like to guarantee flexible childcare.
- Happy Days Nursery has a standard charge of $39 per child per day.
- Happy Days Nursery has a good reputation and is very popular with parents.
Question 3 – Table Analysis
For these, you will be presented with a table containing a large quantity of data. You will be expected to use this data to determine whether three statements are true.
The question below is for illustrative purposes, the table you will see in your test will have a lot more data.
| Name | Last Eruption Date | Height of Volcano (m) | Location | Amount of Lava Produced (cu mi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volcano A | 1712 | 6,450 | Central America | 2.4 |
| Volcano B | 1783 | 3,959 | China | 7.2 |
| Volcano C | 1902 | 5,320 | Alaska | 4.8 |
| Volcano D | 1650 | 6,267 | China | 7.8 |
| Volcano E | 1600 | 4,784 | Alaska | 3.4 |
| Volcano F | 1815 | 4,220 | Central America | 3.1 |
| Volcano G | 1683 | 6,462 | Central America | 5.0 |
Statement 1: In the 17th century, all the volcanoes that erupted were over 5,000 m tall.
Statement 2: Volcanoes in Central America produce larger amounts of lava than other countries.
Statement 3: The amount of lava produced by volcanoes over 5,000 m is always greater than for those less high.
You will need to choose between ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ for each.
Question 4 – Graphics Interpretation
Graphics Interpretation questions consist of a graph or graphic with two sentences underneath. Each sentence will have a few words missing and you will need to find the correct answer from the drop-down menu.
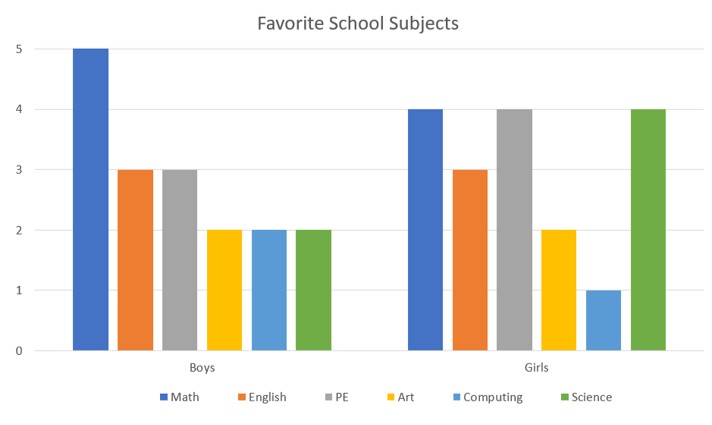
The graph shows the favorite subjects of children in Class 5a St Andrews School.
The subject that is liked 25% more by boys is ___________.
A. Math
B. English
C. PE
D. Art
E. Computing
F. Science
PE is liked by roughly _______ percent of the children in the class.
A. 50%
B. 100%
C. 20%
D. 5%
E. 25%
2. Analytical Writing Assessment
The Analytical Writing Assessment segment of the GMAT has a time allowance of 30 minutes in which the candidate will be expected to write a short essay.
After being presented with an essay prompt, the test taker uses written communication skills to provide analysis and critique of the text.
The prompts will usually be around four to five sentences in length and will present an idea or theory accompanied by supporting evidence. The candidate must then critique the structure of the argument without commenting on the topic itself or trying to suggest alternative theories (points will be deducted for this).
Question 1
In a recent poll, 10% more residents said that they watch movies about historical events than was the case in a poll conducted two years ago. During these past two years, the number of people visiting our city’s history museums has increased by a similar percentage. Since the funding that supports movie production, where history movies are made, is now being threatened with severe cuts, we can expect that attendance at our city’s history museums will also decrease. Thus some of the city’s funds for maintaining historical artifacts should be reallocated to the movie industry.
Question 2
Since a nearby shop, Dress for Less, opened selling discounted clothing, existing clothing shop, Glamorous, has seen a decrease in footfall of around 20%. The best way to increase sales at Glamorous is to reduce their prices to lower than those of Dress for Less until footfall returns to previous levels. The increased footfall will drive up sales, improving takings and then prices can be raised again.
Question 3
Following the success of our premium and most expensive line of salted caramel cake in a recent taste test and the consequent increase in sales, we should shift our business focus to producing additional lines of premium cake rather than our lower-priced, ordinary cakes. With an economic crisis looming, when consumers can no longer buy major luxury items, such as cars, they will still want to indulge in small luxuries, such as expensive cakes.
3. Verbal Reasoning
The Verbal Reasoning part of the test is made up of 36 multiple-choice questions in total, consisting of approximately:
- 10 critical reasoning questions
- 14 sentence correction questions
- 12 reading comprehension questions
The time allowance for this section of the GMAT is 65 minutes.
Question 1 – Critical Reasoning
These questions are about evaluating arguments. You might be asked to identify which of the answer options strengthen or weaken the argument you have been given, or identify assumptions that are being made.
An avid video gamer is statistically more likely to suffer from insomnia than a person who enjoys reading but does not play video games as a habit. It is clear that reading just before bedtime contributes to a more restful night’s sleep, whereas playing video games before bedtime has the opposite effect.
Which of the following, if true, most seriously weakens the above argument?
A. Listening to music before bedtime contributes to restful sleep more than reading does.
B. Insomnia is more common among people who play video games before bed than among people who do not.
C. Engaging in a bedtime activity that is mentally stimulating often interferes with a person’s ability to fall asleep.
D. People who enjoy reading typically like to listen to music just before bedtime.
E. Reading quietly is more conducive to restful sleep than a noisy environment.
Question 2 – Sentence Correction
Here you will be presented with a short paragraph of text, part of it underlined. You will need to identify whether a change needs to be made to the underlined portion to improve grammar or clarity.
Female pheasants are quite plain compared to the adult male pheasant's attractive markings: a colorful plumage, extra-long tail and decorative wattles.
A. the adult male pheasant's
B. those of adult males, their
C. the adult male, which has
D. adult male pheasants'
E. adult males, whose
Question 3 – Reading Comprehension
For the reading comprehension section of the test, the candidate will be presented with a passage of between 250 and 350 words about a subject such as the social sciences, business or humanities. They will then be asked a series of multiple-choice questions about the text to show understanding and analysis.
You may be asked to identify:
- The primary purpose of the passage
- Whether the passage supports or criticizes a certain argument
- Topics that the passage does or does not cover
- The author’s intention/viewpoint
- Inferences that the author is making
4. Quantitative Reasoning
Made up of 31 multiple-choice questions and with a time allowance of 62 minutes, the Quantitative Reasoning section of the GMAT is split into two areas:
- Problem-Solving
- Data Sufficiency
Question 1 – Problem-Solving
These are usually math-based questions that will test your problem-solving ability.
If d > c, a > e, b > c and c > a, which of the following must be true?
1. d > b
2. b > e
3. d > a
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 3
Question 2 – Data Sufficiency
Every question in the Data Sufficiency section asks the same thing: is the information given enough to answer the question? You will always have the same answer options.
Let’s use an example:
Is x > 9?
1. x > 8
2. x > 7
The candidate needs to work out which, if any, of the two answer options are enough to answer the question.
A. 1 is enough, 2 is not
B. 2 is enough, 1 is not
C. You need both statements
D. 1 is enough alone and 2 is enough alone
E. You can’t answer the question


